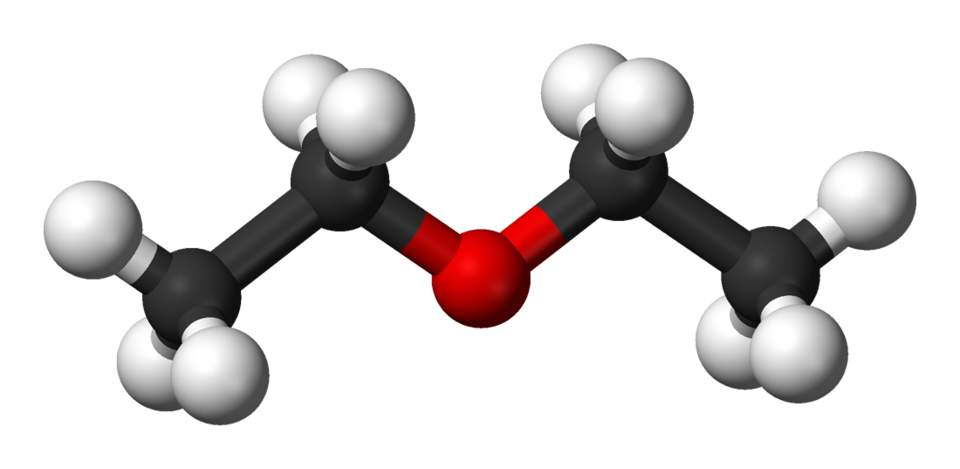
The ethoxyethane chemical formula is a fascinating doorway into the world of organic chemistry. Known commonly as diethyl ether, this compound has played a pivotal role in both historical and modern scientific developments. From its early use as an anaesthetic to its current role as a vital laboratory solvent, ethoxyethane continues to be an essential compound worth understanding in depth.
Its molecular structure and properties reveal why it’s so useful—and potentially dangerous—in both educational and industrial settings. This article explores the ethoxyethane chemical formula, structure, applications, and its relationship to other important chemical substances, offering a complete guide for students, researchers, and curious minds alike.
Ethoxyethane chemical formula explained clearly
The ethoxyethane chemical formula is represented as (C₂H₅)₂O or more simply as C₄H₁₀O. This indicates the presence of two ethyl groups (C₂H₅) connected via a single oxygen atom. The structure is symmetrical and defines ethoxyethane as part of the ether family—organic compounds characterised by an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.
This chemical arrangement gives ethoxyethane several important features. Unlike water or alcohols, ethoxyethane cannot form hydrogen bonds with itself, leading to a relatively low boiling point and high volatility. These molecular features are essential for understanding its use in chemistry, particularly in extraction processes where low-polarity solvents are needed.
Structural identity and IUPAC naming system
The IUPAC name for diethyl ether is ethoxyethane, which follows systematic naming rules. The ‘ethoxy’ prefix refers to an ethyl group bonded to oxygen, while ‘ethane’ refers to the second ethyl group it is attached to. The formula is often condensed to CH₃CH₂–O–CH₂CH₃, which visually represents how the atoms are connected.
This structural simplicity is one reason ethoxyethane became such an important molecule in organic chemistry. The ether linkage (R–O–R) is relatively stable, non-reactive, and able to dissolve many substances that cannot be dissolved in water. This makes the ethoxyethane chemical formula a common sight in lab settings, particularly when handling non-polar compounds or sensitive reactions.
Physical and chemical properties of ethoxyethane

Ethoxyethane is a colourless, sweet-smelling liquid that evaporates rapidly at room temperature. Its boiling point is 34.6°C, and it has a melting point of −116.3°C. Its low density (approximately 0.713 g/cm³) means it floats on water, yet it doesn’t dissolve in water easily due to its low polarity.
It is highly flammable, with vapours that can form explosive mixtures with air. That makes its handling in laboratories strictly regulated. Despite its volatility, it is chemically stable under normal conditions and does not react with most bases or dilute acids. However, prolonged exposure to oxygen can lead to the formation of peroxides—unstable and dangerous compounds that must be carefully managed.
Applications and real-world uses of ethoxyethane
The ethoxyethane chemical formula makes this compound ideal for use as a solvent in organic chemistry. Its ability to dissolve oils, waxes, and non-polar molecules makes it highly versatile in laboratories and the chemical manufacturing industry. It is often used during extractions, crystallisations, and reactions requiring an inert medium.
In history, ethoxyethane was used as one of the earliest general anaesthetics. Although it has been replaced by safer alternatives, its legacy in medical science is firmly established. Today, it’s primarily found in chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and even as a starter fluid for petrol engines due to its flammable nature and volatility.
Understanding ethoxyethane through comparisons
To better understand the ethoxyethane chemical formula, it helps to compare it to other well-known chemical compounds. For instance, the chemical formula for salt is NaCl, a simple ionic compound. In contrast, ethoxyethane is covalent and organic. The chemical formula for sugar (sucrose) is C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁, far more complex and polar than ethoxyethane.
Other familiar examples include methane (CH₄), a basic hydrocarbon gas, and ammonia (NH₃), a nitrogen-based base used in cleaning products. Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), alcohol (ethanol – C₂H₅OH), and methanol (CH₃OH) are also structurally distinct, yet serve different roles in biology and chemistry. These comparisons highlight just how unique and specialised the ethoxyethane molecule really is.
Chemical safety and toxicology insights
One cannot discuss ethoxyethane without addressing safety. As a volatile organic compound, it poses significant risks if misused. Vapour inhalation may cause dizziness, headache, or unconsciousness in high concentrations. It’s also extremely flammable, so even small sparks can ignite dangerous fires if proper care is not taken.
In discussing related risks, it’s important to remember that incomplete combustion of fuels like petrol or propane produces carbon monoxide—a highly poisonous gas with no smell or colour. While this isn’t a property of ethoxyethane itself, it’s vital to recognise the broader dangers of working with flammable organic compounds in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas.
Why knowing chemical formulas matters
Understanding the ethoxyethane chemical formula goes beyond memorisation. It teaches us how to interpret molecular structures, predict chemical behaviour, and choose appropriate compounds for specific tasks. Whether you’re studying chemistry or working in a laboratory, having a solid grasp of chemical formulas boosts safety, efficiency, and scientific insight.
Formulas also allow for the classification of substances. For instance, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a strong base, while sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a powerful acid. Knowing the difference helps avoid dangerous reactions. Similarly, aspirin (C₉H₈O₄), propane (C₃H₈), and diamond (C) all tell very different stories through their unique formulas—just like ethoxyethane does.
Conclusion
The ethoxyethane chemical formula offers far more than just a label. It opens up a gateway to understanding organic chemistry, solvent behaviour, and safe laboratory practices. With a simple but effective structure, it stands as a symbol of how molecular design shapes practical use. From flammable liquid to versatile solvent, ethoxyethane remains an essential player in both classroom and professional chemistry.
Exploring this compound helps us appreciate the broader landscape of chemical science—from the structure of table salt to the properties of alcohols and hydrocarbons. The more we know about substances like ethoxyethane, the better equipped we are to innovate, explore, and stay safe in the chemical world.
FAQs
What is the chemical formula of ethoxyethane?
The chemical formula is (C₂H₅)₂O or C₄H₁₀O, showing two ethyl groups joined by an oxygen atom.
Is ethoxyethane the same as diethyl ether?
Yes, ethoxyethane is the IUPAC name for diethyl ether. Both refer to the same compound.
What is ethoxyethane used for?
It is primarily used as a solvent in organic chemistry, and historically as an anaesthetic.
Is ethoxyethane flammable?
Extremely. It has a low flash point and can form explosive mixtures with air.
What poisonous gas is released by incomplete combustion?
The gas is carbon monoxide, a deadly, odourless compound.
You may also read: List of Cancer Charities UK: Top 20 Trusted Charities for Support and Donations